Description
Qjazz-Processes is an draft implementation of the OGC Processes api standards Open Geospatial Consortium based on the QGIS Processing API.
This implementation allows you to expose and run on a server:
QGIS Processing models and scripts
QGIS plugins having a Processing provider according to their
metadata.txtfile
Features
Asynchronous
Horizontally scalable
Routing specifications
Handle schemas for all Qgis parameters
OAPI compliant
Requirements and limitations
Linux/Posix OS
Python 3.12+ only
Redis server
RabbitMQ server
QGIS 3.34+
Overview
Qjazz-Processes is built on top of the Celery framework.
A Qjazz-Processes Celery Worker expose the necessary tasks for
Listing exposed Qgis algorithms as OGC processes
Returning process description
Executing a Qgis algorithm
A Qjazz-Processes Server expose an OGC processes compliant api and handle messages and results from the Worker.
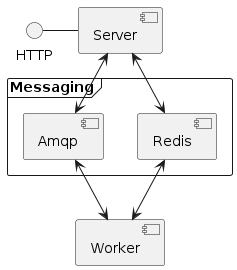
The simplest configuration
Running multiple workers and servers
Worker and servers and independant components and you may run any server and workers as different services on different environments.
This enable running workers in different environments and infrastructure according to your requirements.
You may for example have a worker running intensive Jobs on a dedicated pool of machine/vm while other jobs may be run on smallest architecture.
Some wokers may run on specific environments likes different Qgis versions or using specific libraries
Services
Each worker is bound to a service that represents a set of Qgis processing providers and Qgis projects.
The Server route execution messages to specific services: how routing is done depends on the selected access policy from the configuration.
The default access policy select the service from the service query parameter or take the first
available service. Other acces policy will consider a pecific header and much more sophisticated
routing can be achieve by implementing custom access policy.
Since we run Celery behind the scene, there is no need to declare the services to the front end servers; once a worker is deployed, it will be known known to the servers after some time depending on the configured update interval.
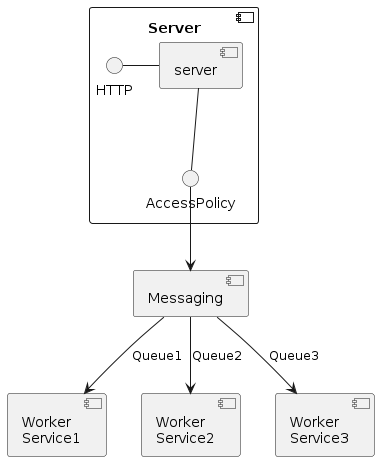
A more complex configuration with multiple services
Quick start
Docker compose setup
This is the recommended way to install and run the services:
The simplest configuration for basic working installation is the following
services:
worker:
image: 3liz/qjazz:qgis-ltr
environment:
CONF_LOGGING__LEVEL: DEBUG
CONF_WORKER__SERVICE_NAME: "MyService"
CONF_WORKER__BROKER_HOST: rabbitmq
CONF_WORKER__BACKEND_HOST: redis:6379/0
CONF_PROCESSING__WORKDIR: /qgis-workdir
CONF_PROCESSING__PLUGINS__PATHS: >-
["/qgis-plugins"]
CONF_PROCESSING__PROJECTS__SEARCH_PATHS: >-
{
"/":"/qgis-projects"
}
depends_on:
- rabbitmq
volumes:
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/workdir/", target: /qgis-workdir }
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/plugins/", target: /qgis-plugins }
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/projects", target: /qgis-projects }
command: ["qjazz-processes", "worker"]
server:
image: 3liz/qjazz:qgis-ltr
ports:
- 127.0.0.1:9080:9080
command: ["qjazz-processes", "serve", "-v"]
environment:
CONF_EXECUTOR__CELERY__BROKER_HOST: rabbitmq
CONF_EXECUTOR__CELERY__BACKEND_HOST: redis:6379/0
rabbitmq:
image: rabbitmq:3-alpine
redis:
image: redis:6-alpine
Alternatively you may use a configuration file:
services:
worker:
image: 3liz/qjazz:qgis-ltr
depends_on:
- rabbitmq
volumes:
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/worker.toml", target: /worker.toml }
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/workdir/", target: /qgis-workdir }
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/plugins/", target: /qgis-plugins }
- { type: bind, source: "/path/to/projects", target: /qgis-projects }
command: ["qjazz-processes", "worker", "-C", "/etc/worker.toml"]
server:
image: 3liz/qjazz:qgis-ltr
ports:
- 127.0.0.1:9080:9080
command: ["qjazz-processes", "serve", "-v"]
environment:
CONF_EXECUTOR__CELERY__BROKER_HOST: rabbitmq
CONF_EXECUTOR__CELERY__BACKEND_HOST: redis:6379/0
rabbitmq:
image: rabbitmq:3-alpine
redis:
image: redis:6-alpine
With the worker.toml configuration file:
[worker]
service_name = "MyService"
backend_host = "redis:6379/0"
broker_host = "rabbitmq"
[processing]
workdir = "/qgis-workdir"
[processing.plugins]
paths = ["/qgis-plugins"]
[processing.projects.search_paths]
'/' = "/qgis-projects"
The Qjazz-Processes applications take care of configuring Celery for using Redis and RabbitMQ so you usually do not have to deal directly with the Redis or RabbitMQ setup.
For more details, refer to https://docs.celeryq.dev/en/stable/getting-started/backends-and-brokers/rabbitmq.html and https://docs.celeryq.dev/en/stable/getting-started/backends-and-brokers/redis.html for how they are configured with Celery
Installing from source
You can install directly from source by cloning the reposittory and
running make install for installing all python modules.
Running the worker and the server is as simple as:
qjazz-processing serve -C <worker-configuration-file>
and
qjazz-processes server -C <server-configuration-file>
Warning
--system-site-packages option so that you can
access PyQGIS modules.